Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- CSS
- 리액트
- css기초
- 코딩테스트
- 자바스크립트
- 백준nodejs
- 코테
- 알고리즘
- HTML5
- JS
- 백준js
- 리액트댓글기능
- 백준알고리즘
- js코테
- 포이마웹
- 백준구현문제
- 백준
- dp알고리즘
- 백준골드
- 몽고DB
- 백준구현
- 프로그래머스코테
- JS프로그래머스
- 프로그래머스
- 다이나믹프로그래밍
- 안드로이드 스튜디오
- 리액트커뮤니티
- 익스프레스
- 프로그래머스JS
- HTML
Archives
- Today
- Total
개발새발 로그
[2023-09-26] TIL - 자료구조 & 알고리즘 - 트라이(Trie) 본문

구글이나 네이버 검색에서 자동완성을 하려면 어떻게 해야할까?
이런 경우에 사용하기에 적합한 자료 구조로 트라이(Trie) 가 있다.
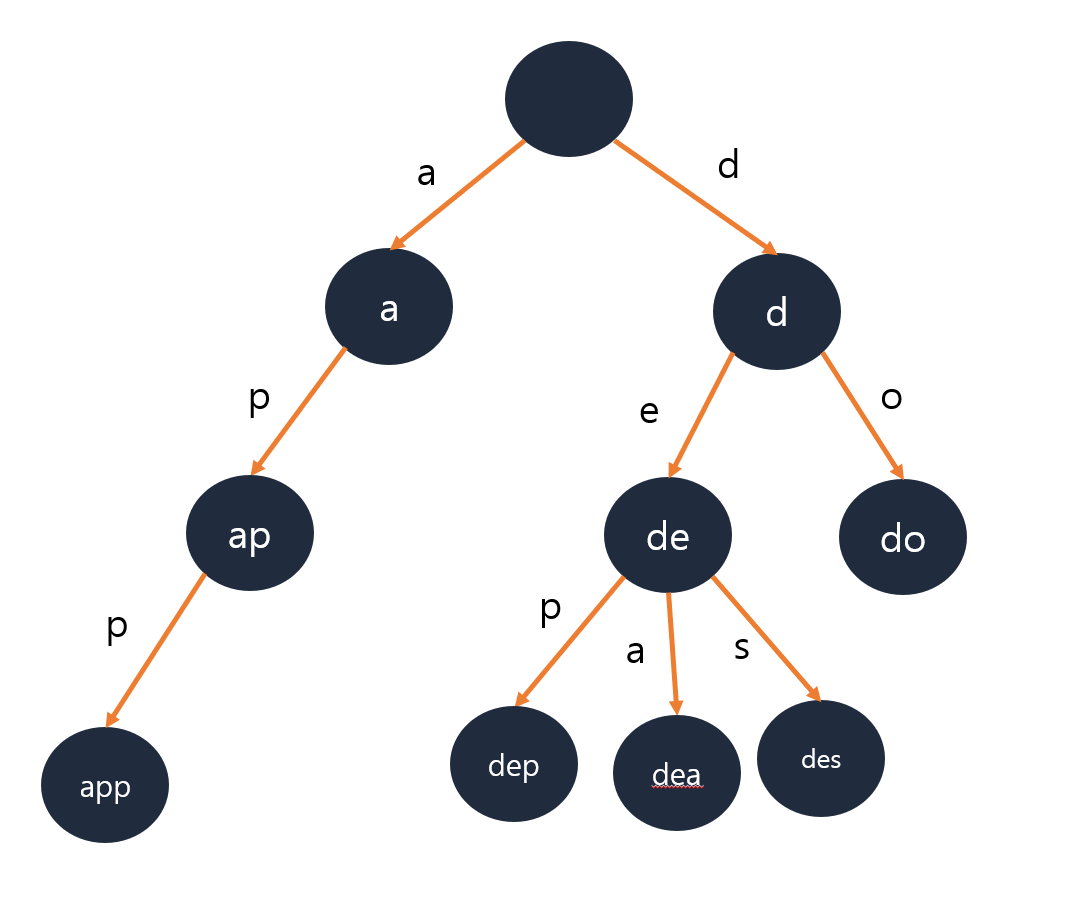
트라이
- 문자열을 저장하고 효율적으로 탐색하기 위한 트리 형태의 구조
트라이의 특징
- 검색어 자동완성, 사전 찾기 등에 응용될 수 있다.
- 문자열을 탐색할 때 단순하게 비교하는 것보다 효율적으로 찾을 수 있다.
- L이 문자열의 길이일 때, 삽입은 O(L)만큼 걸린다.
- 대신 각 정점이 자식에 대한 링크를 전부 가지고 있기에 더 많은 저장공간을 사용한다.
Trie 생성하기
Trie 구조
- 루트는 비어있다.
- 각 간선은 추가될 문자를 키로 가진다.
- 각 정점은 이전 정점의 값 + 간선의 키를 값으로가진다.
- 해시테이블과 연결리스트를 이용하여 구현할 수 있다.
자바스크립트로 Trie 구현하기
class Node {
// 그래프 처럼 노드가 필요
// 인접리스트 형태로 구현
constructor(value = "") {
this.value = value;
this.children = new Map();
}
}
class Trie {
// Trie는 루트가 빈 노드이다.
constructor() {
this.root = new Node();
}
insert(string) {
// 루트부터 탐색을 하기 위함
let currentNode = this.root;
// 문자열을 하나씩 자르면선 순회한다.
for(const char of string) {
//만약 현재 노드에서 자른 문자열을 간선으로 가지고 있지 않다면 새롭게 노드를 추가한다.
if(!currentNode.children.has(char)) {
currentNode.children.set(
char,
new Node(currentNode.value + char)
);
}
//다음 정점으로 이동한다.
// 이 루프를 반복하면 문자열을 전부 요소로 추가할 수 있다.
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
}
has(string) {
//추가를 응용
let currentNode = this.root;
for(const char of string) {
if(!currentNode.children.has(char)) {
return false;
}
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
return true;
}
}
const trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("cat");
trie.insert("can");
console.log(trie.has("cat")); // true
자동완성 코드
-while문으로 자동완성단어를 찾음
class Node {
constructor(value = "") {
this.value = value;
this.children = new Map();
this.end = false; // 단어의 끝을 알려주는 데이터
}
}
class Trie {
constructor() {
this.root = new Node();
}
insert(string) {
// 루트부터 탐색을 하기 위함
let currentNode = this.root;
// 문자열을 하나씩 자르면서 순회한다.
for (const char of string) {
//만약 현재 노드에서 자른 문자열을 간선으로 가지고 있지 않다면 새롭게 노드를 추가한다.
if (!currentNode.children.has(char)) {
// 저장할 때 [자른 문자, 하위 노드를 위한 Node 클래스와 해당 value값은 currentNode.value + char]
currentNode.children.set(char, new Node(currentNode.value + char));
}
//다음 정점으로 이동한다.
// 이 루프를 반복하면 문자열을 전부 요소로 추가할 수 있다.
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
currentNode.end = true;
}
has(string) {
//추가를 응용
let currentNode = this.root;
for (const char of string) {
if (!currentNode.children.has(char)) {
return false;
}
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
const search = []; // 검색어 자동완성을 저장할 배열
const stack = []; // 스택에 현재 노드와 자동완성되는 문자를 누적함
stack.push([currentNode, string]);
while (stack.length > 0) {
//현재 노드와 탐색하려는 word를 빼줌
const [node, word] = stack.pop();
//만약 현재 노드가 단어의 끝이라면 이전까지 누적된 단어를 serach에 넣어줌
if (node.end) {
search.push(word);
}
//현재 노드의 자식을 배열구조로 만들고 구조분해할당
for (const [str, strChild] of node.children.entries()) {
//현재 노드에서 갈 수 있는 자식 노드를 순회하고 그 노드들을 stack에 넣는다.
stack.push([strChild, word + str]);
}
}
return search;
}
}
const trie = new Trie();
const words = ["apple", "application", "app", "cat", "can", "call"];
words.forEach((word) => trie.insert(word));
const str = "app";
console.log(trie.has(str));
-재귀로 자동완성단어를 찾음
class Node {
constructor(value = "") {
this.value = value;
this.children = new Map();
this.end = false; // 단어의 끝을 알려주는 데이터
}
}
class Trie {
constructor() {
this.root = new Node();
}
insert(string) {
// 루트부터 탐색을 하기 위함
let currentNode = this.root;
// 문자열을 하나씩 자르면선 순회한다.
for (const char of string) {
//만약 현재 노드에서 자른 문자열을 간선으로 가지고 있지 않다면 새롭게 노드를 추가한다.
if (!currentNode.children.has(char)) {
currentNode.children.set(char, new Node(currentNode.value + char));
}
//다음 정점으로 이동한다.
// 이 루프를 반복하면 문자열을 전부 요소로 추가할 수 있다.
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
currentNode.end = true;
}
has(string) {
//추가를 응용
let currentNode = this.root;
for (const char of string) {
if (!currentNode.children.has(char)) {
return false;
}
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
//만약 검색하려는 단어가 온전히 있다면 find 함수를 수행
// 자동완성 검색어를 저장할 배열
const search = [];
this.find(currentNode, string, search);
return search;
}
//find 함수가 재귀적으로 흘러감
find(currentNode, string, search) {
//재귀적으로 흘러가다가 단어의 끝을 만나면 자동완성 검색어 배열에 누적하던 string을 저장한다.
if (currentNode.end) {
search.push(string);
}
console.log(currentNode.children.entries().next().value);
//현재 노드인 char과 그 자식 노드인 childNode
for (const [char, childNode] of currentNode.children.entries()) {
this.find(childNode, string + char, search);
}
}
}
const trie = new Trie();
const words = ["apple", "application", "app", "cat", "can", "call"];
words.forEach((word) => trie.insert(word));
const str = "app";
console.log(trie.has(str));
728x90
반응형
LIST
'TIL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [2023-09-27] TIL - 자료구조 & 알고리즘 - 이진탐색 (0) | 2023.09.27 |
|---|---|
| [2023-09-26] TIL - 자료구조 & 알고리즘 - 정렬 (0) | 2023.09.27 |
| [2023-09-26] 자료구조 & 알고리즘 - 힙 (0) | 2023.09.26 |
| [2023-09-26] TIL - 자료구조 & 알고리즘 - 트리 (0) | 2023.09.26 |
| [2023-09-25] 자료구조 & 알고리즘 - 그래프 (0) | 2023.09.25 |